Webhooks
Introduction
A webhook is a mechanism that allows an application to send notifications or data to another application in real time via a specified URL. It is commonly used to automate processes and synchronise information between different systems.
This mechanism relies on trigger events which, when they occur, send an HTTP POST request containing event-specific information. Webhooks are particularly useful in scenarios where real-time updates are essential, such as payment notifications, order status updates, or integrations between applications.
Configuring a Webhook
To configure a webhook, go to this URL. You will need to specify a destination URL that will be called by the source application.
This URL must be able to process the received data and respond with an appropriate HTTP status to confirm receipt.
| Property | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
name | Name of the webhook | String |
description | Description of the webhook | String |
url | URL of the webhook | String |
headers | Headers of the webhook | HashMap<String, String> |
headers[n].key | Key of the header | String |
headers[n].value | Value of the header | String |
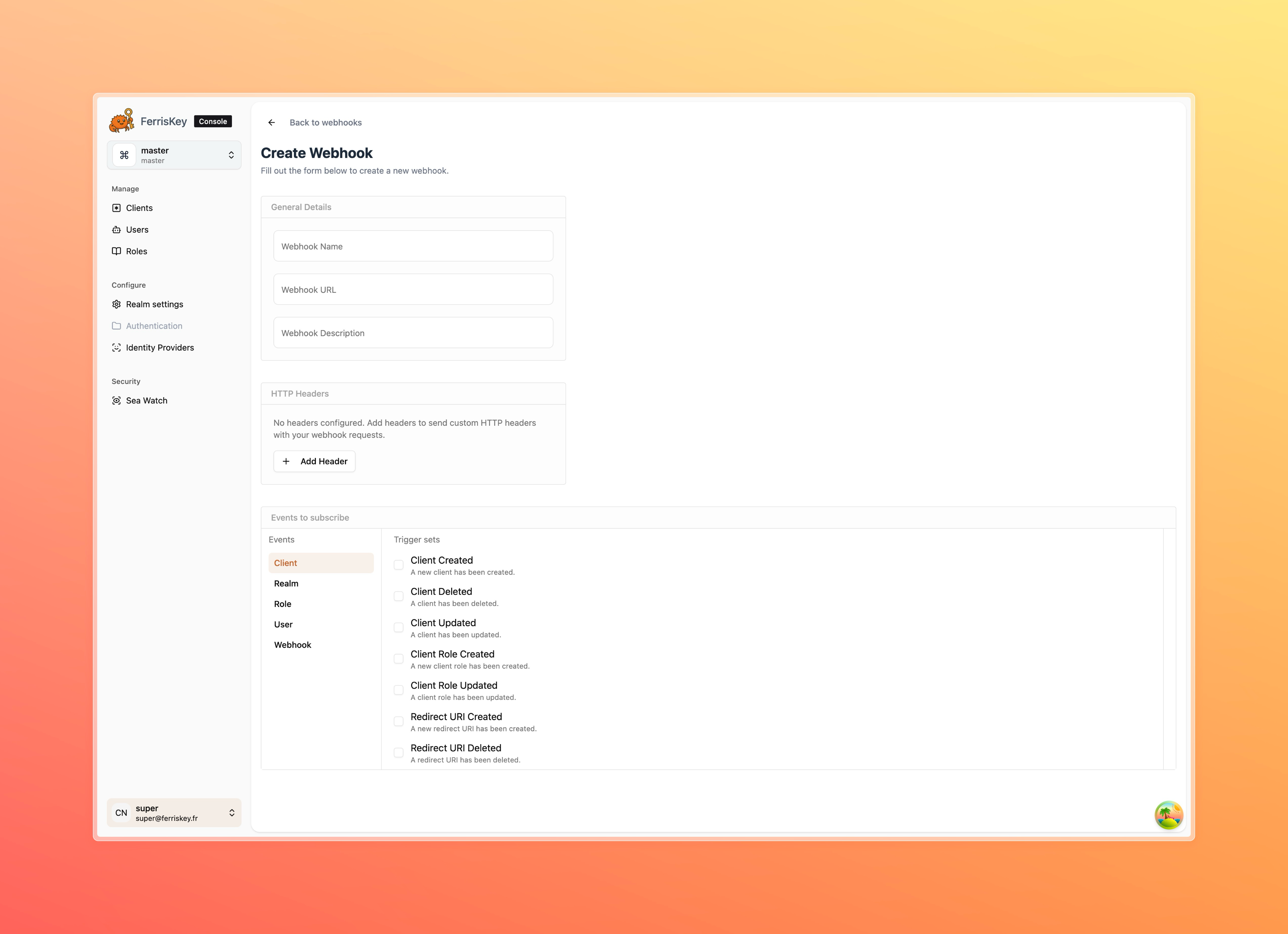
Events
Now that your webhook is declared, you must choose the set of events you wish to subscribe to for this webhook.
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
user.created | Triggered when a user is created. |
user.updated | Triggered when a user is updated. |
user.deleted | Triggered when a user is deleted. |
user.role.assigned | Triggered when a role is assigned to a user. |
user.role.unassigned | Triggered when a role is unassigned from a user. |
user.bulk_deleted | Triggered when multiple users are deleted. |
user.credentials.deleted | Triggered when a user's credentials are deleted. |
auth.reset_password | Triggered when a password reset is initiated. |
client.created | Triggered when a client is created. |
client.updated | Triggered when a client is updated. |
client.deleted | Triggered when a client is deleted. |
client.role.created | Triggered when a role is created for a client. |
client.role.updated | Triggered when a role is updated for a client. |
redirect_uri.created | Triggered when a redirect URI is created. |
redirect_uri.updated | Triggered when a redirect URI is updated. |
redirect_uri.deleted | Triggered when a redirect URI is deleted. |
role.created | Triggered when a role is created. |
role.updated | Triggered when a role is updated. |
role.deleted | Triggered when a role is deleted. |
role.permission.updated | Triggered when permissions of a role are updated. |
realm.created | Triggered when a realm is created. |
realm.updated | Triggered when a realm is updated. |
realm.deleted | Triggered when a realm is deleted. |
realm.settings.updated | Triggered when realm settings are updated. |
webhook.created | Triggered when a webhook is created. |
webhook.updated | Triggered when a webhook is updated. |
webhook.deleted | Triggered when a webhook is deleted. |
Receive event
To receive and process webhook events, you need to set up an endpoint that listens for incoming HTTP POST requests. Below is an example implementation in Rust using the Axum framework. This example demonstrates how to handle incoming webhook payloads and log the event details.
Make sure to replace the placeholder types and logic with your specific requirements.
use axum::{
routing::post,
Router,
Json,
};
use serde::Deserialize;
use std::net::SocketAddr;
use tokio;
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() {
// Build the application with a POST route
let app = Router::new().route("/webhook", post(handle_webhook));
// Define the address to bind the server
let addr = SocketAddr::from(([127, 0, 0, 1], 3000));
println!("Server running on {}", addr);
// Start the server
axum::Server::bind(&addr)
.serve(app.into_make_service())
.await
.unwrap();
}
// Define the structure of the incoming JSON payload
#[derive(Deserialize)]
struct WebhookPayload {
pub event: WebhookTrigger,
pub timestamp: String,
pub resource_id: Uuid,
// Depend on the event type
pub data: T,
}
// Handler for the POST route
async fn handle_webhook(Json(payload): Json<WebhookPayload>) {
println!("Received event: {}", payload.event);
println!("Payload data: {}", payload.data);
}
